Ketogenic Amino Acids Definition
Ketogenic Amino Acids Definition. Description of amino acid structure absolute configuration at the α carbon. All amino acids have a high melting point greater than 200 o; Amino acids are colorless, crystalline solid. This property is involved in glutamate and gaba. They include all amino acids except lysine and leucine [3].
Description of amino acid structure absolute configuration at the α carbon. This property is involved in glutamate and gaba. They are soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and dissolve with difficulty in methanol, ethanol, and propanol. There are 20 amino acids encoded by the standard human genetic code. In the human body, glucogenic amino acids can be converted to glucose in the process called gluconeogenesis;
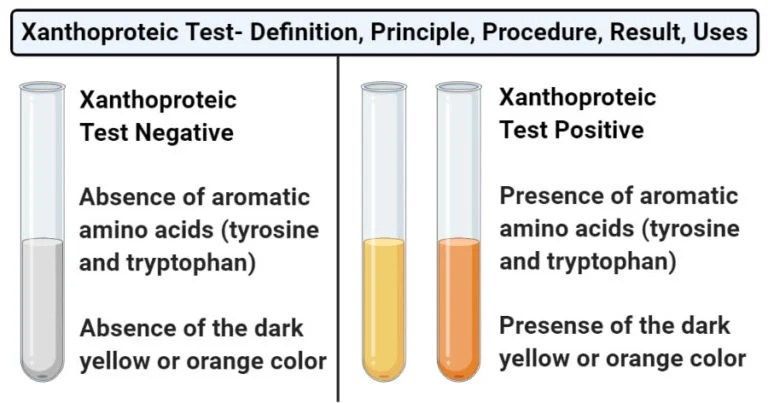 Xanthoproteic Test- Definition, Principle, Procedure from i0.wp.com
Xanthoproteic Test- Definition, Principle, Procedure from i0.wp.com
All amino acids have a high melting point greater than 200 o; As shown here, most amino acids are converted to intermediates of the citric acid cycle or to pyruvate, which in turn can serve as precursors for gluconeogenesis; Amino acids are colorless, crystalline solid. Ketogenic amino acids, which can be converted to ketones: The diet forces the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrates. Jul 06, 2021 · properties of amino acids. Catabolism of fatty acids in the liver produces ketone bodies (kb), which induces urinary ketosis. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−nh + 3) and carboxylate −co − 2 functional groups, along with a side chain (r group) specific to each amino acid.
Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids.
This property is involved in glutamate and gaba. The remaining 11 amino acids are nonessential amino acids. They include all amino acids except lysine and leucine [3]. Jul 06, 2021 · properties of amino acids. Amino acids are colorless, crystalline solid. They must be obtained from the diet. The diet mimics the fasting state, altering the metabolism to use fats as a primary fuel source; On the basis of the metabolic fate of the amino acids, they … Normally carbohydrates in food are converted into glucose, which is then transported around the body and is important in fueling brain function. As shown here, most amino acids are converted to intermediates of the citric acid cycle or to pyruvate, which in turn can serve as precursors for gluconeogenesis; Ketogenic and glucogenic amino acids mnemonic. The diet forces the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrates. Those amino acids that yield acetoacetate are called ketogenic, since acetoacetate is one of the ketone bodies (see slide 10.4).
Catabolism of fatty acids in the liver produces ketone bodies (kb), which induces urinary ketosis. They are soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and dissolve with difficulty in methanol, ethanol, and propanol. Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids. This property is involved in glutamate and gaba. Ketogenic amino acids, which can be converted to ketones:
 Xanthoproteic Test- Definition, Principle, Procedure from i0.wp.com
Xanthoproteic Test- Definition, Principle, Procedure from i0.wp.com
There are 20 amino acids encoded by the standard human genetic code. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−nh + 3) and carboxylate −co − 2 functional groups, along with a side chain (r group) specific to each amino acid. In the human body, glucogenic amino acids can be converted to glucose in the process called gluconeogenesis; Description of amino acid structure absolute configuration at the α carbon. The remaining 11 amino acids are nonessential amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and polypeptides.these are organic compounds composed of c, h, o and n atoms. Normally carbohydrates in food are converted into glucose, which is then transported around the body and is important in fueling brain function. Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids.
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−nh + 3) and carboxylate −co − 2 functional groups, along with a side chain (r group) specific to each amino acid.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and polypeptides.these are organic compounds composed of c, h, o and n atoms. Ketogenic and glucogenic amino acids mnemonic. In addition sulfur (s) is present in the side chains of cysteine and methionine, and selenium (se) in the less common. The degradative pathways can be divided into two major classes. This property is involved in glutamate and gaba. These are the glucogenic amino acids. Normally carbohydrates in food are converted into glucose, which is then transported around the body and is important in fueling brain function. There are 20 amino acids encoded by the standard human genetic code. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−nh + 3) and carboxylate −co − 2 functional groups, along with a side chain (r group) specific to each amino acid. The diet forces the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrates. They must be obtained from the diet. However, knowledge of which amino acids are essential is beyond the scope of what you need to know. Ketogenic amino acids, which can be converted to ketones:
Description of amino acid structure absolute configuration at the α carbon. This property is involved in glutamate and gaba. In addition sulfur (s) is present in the side chains of cysteine and methionine, and selenium (se) in the less common. The diet mimics the fasting state, altering the metabolism to use fats as a primary fuel source; As shown here, most amino acids are converted to intermediates of the citric acid cycle or to pyruvate, which in turn can serve as precursors for gluconeogenesis;
 Define Your Delts: 5 Must-Do Shoulder Exercises from i1.wp.com
Define Your Delts: 5 Must-Do Shoulder Exercises from i1.wp.com
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−nh + 3) and carboxylate −co − 2 functional groups, along with a side chain (r group) specific to each amino acid. The diet forces the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrates. This property is involved in glutamate and gaba. They are soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and dissolve with difficulty in methanol, ethanol, and propanol. Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids. They include all amino acids except lysine and leucine [3]. All amino acids have a high melting point greater than 200 o; Description of amino acid structure absolute configuration at the α carbon.
Ketogenic and glucogenic amino acids mnemonic.
Description of amino acid structure absolute configuration at the α carbon. Isoleucine, leucine, lysine, phenylalanine, threonine, thryptophan and tyrosine. The diet forces the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrates. The elements present in every amino acid are carbon (c), hydrogen (h), oxygen (o), and nitrogen (n); In the human body, glucogenic amino acids can be converted to glucose in the process called gluconeogenesis; 10 of the amino acids are considered essential amino acids for humans since the human body cannot produce them; Ketogenic amino acids, which can be converted to ketones: They include all amino acids except lysine and leucine [3]. The diet mimics the fasting state, altering the metabolism to use fats as a primary fuel source; Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and polypeptides.these are organic compounds composed of c, h, o and n atoms. All amino acids have a high melting point greater than 200 o; Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−nh + 3) and carboxylate −co − 2 functional groups, along with a side chain (r group) specific to each amino acid. They are soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and dissolve with difficulty in methanol, ethanol, and propanol.
They include all amino acids except lysine and leucine [3][ketogenic amino acids](https://security-systems-small-business.pages.dev/posts/ketogenic-amino-acids) 10 of the amino acids are considered essential amino acids for humans since the human body cannot produce them;
However, knowledge of which amino acids are essential is beyond the scope of what you need to know. Isoleucine, leucine, lysine, phenylalanine, threonine, thryptophan and tyrosine. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and polypeptides.these are organic compounds composed of c, h, o and n atoms. Catabolism of fatty acids in the liver produces ketone bodies (kb), which induces urinary ketosis. They include all amino acids except lysine and leucine [3].
Source: i1.wp.com
Jul 06, 2021 · properties of amino acids. All amino acids have a high melting point greater than 200 o; They include all amino acids except lysine and leucine [3]. As shown here, most amino acids are converted to intermediates of the citric acid cycle or to pyruvate, which in turn can serve as precursors for gluconeogenesis; In the human body, glucogenic amino acids can be converted to glucose in the process called gluconeogenesis;
Source: i0.wp.com
The elements present in every amino acid are carbon (c), hydrogen (h), oxygen (o), and nitrogen (n); The remaining 11 amino acids are nonessential amino acids. As shown here, most amino acids are converted to intermediates of the citric acid cycle or to pyruvate, which in turn can serve as precursors for gluconeogenesis; Jul 06, 2021 · properties of amino acids. They include all amino acids except lysine and leucine [3].
Source: i1.wp.com
In addition sulfur (s) is present in the side chains of cysteine and methionine, and selenium (se) in the less common. However, knowledge of which amino acids are essential is beyond the scope of what you need to know. The degradative pathways can be divided into two major classes. Normally carbohydrates in food are converted into glucose, which is then transported around the body and is important in fueling brain function. Some amino acids can be converted into glucose while others can be converted to ketone bodies.
Source: i0.wp.com
They are soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and dissolve with difficulty in methanol, ethanol, and propanol. They must be obtained from the diet. The elements present in every amino acid are carbon (c), hydrogen (h), oxygen (o), and nitrogen (n); The diet mimics the fasting state, altering the metabolism to use fats as a primary fuel source; Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−nh + 3) and carboxylate −co − 2 functional groups, along with a side chain (r group) specific to each amino acid.
Source: i0.wp.com
Those amino acids that yield acetoacetate are called ketogenic, since acetoacetate is one of the ketone bodies (see slide 10.4). Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−nh + 3) and carboxylate −co − 2 functional groups, along with a side chain (r group) specific to each amino acid. They include all amino acids except lysine and leucine [3]. Ketogenic and glucogenic amino acids mnemonic. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and polypeptides.these are organic compounds composed of c, h, o and n atoms.
Source: i0.wp.com
This property is involved in glutamate and gaba. They are soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and dissolve with difficulty in methanol, ethanol, and propanol. The remaining 11 amino acids are nonessential amino acids. There are 20 amino acids encoded by the standard human genetic code. All amino acids have a high melting point greater than 200 o;
Source: i0.wp.com
The elements present in every amino acid are carbon (c), hydrogen (h), oxygen (o), and nitrogen (n); Ketogenic amino acids, which can be converted to ketones: Some amino acids can be converted into glucose while others can be converted to ketone bodies. The diet forces the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrates. The remaining 11 amino acids are nonessential amino acids.
Source: i1.wp.com
Amino acids are colorless, crystalline solid. There are 20 amino acids encoded by the standard human genetic code. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and polypeptides.these are organic compounds composed of c, h, o and n atoms. Description of amino acid structure absolute configuration at the α carbon. These are the glucogenic amino acids.
10 of the amino acids are considered essential amino acids for humans since the human body cannot produce them;
Source: i0.wp.com
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and polypeptides.these are organic compounds composed of c, h, o and n atoms.
Source: i0.wp.com
They must be obtained from the diet.
Source: i0.wp.com
Jul 06, 2021 · properties of amino acids.
Source: i1.wp.com
Those amino acids that yield acetoacetate are called ketogenic, since acetoacetate is one of the ketone bodies (see slide 10.4).
Source: i1.wp.com
There are 20 amino acids encoded by the standard human genetic code.
Source: i1.wp.com
They are soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and dissolve with difficulty in methanol, ethanol, and propanol.
Source: i0.wp.com
As shown here, most amino acids are converted to intermediates of the citric acid cycle or to pyruvate, which in turn can serve as precursors for gluconeogenesis;
Source: i1.wp.com
In addition sulfur (s) is present in the side chains of cysteine and methionine, and selenium (se) in the less common.